When comparing AI agents vs chatbots vs virtual assistants, the differences can be confusing. While all three improve digital interactions, their functions, complexity, and business value vary.
In this guide, we’ll break down definitions, key differences, real-world examples, pros & cons, and use cases so you can choose the right solution for your business.
An AI agent is a software program that can autonomously perform tasks, make decisions, and solve problems without constant human supervision. Unlike traditional automation, AI agents continuously learn from interactions, adapt to new data, and execute complex workflows.
👉 Think of an AI agent as a proactive digital partner rather than just a tool.
Key Features of AI Agents:
Examples of AI Agents in Business:
📊 Market Insight: The global AI agents market is forecasted at USD 7.92 billion in 2025 and could expand to USD 236.03 billion by 2034, with a remarkable CAGR of ~45.82%. This explosive growth highlights the rising demand for autonomous, proactive AI systems in enterprise workflows.
Mini-Summary: AI agents are proactive, strategic, and learning-driven, making them ideal for automation, analytics, and predictive decision-making.
If you’d like a deeper dive into what AI agents are, their types, and practical examples, don’t miss our full guide here: AI Agents: Definition, Examples and Types
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate conversation with human users, typically via messaging apps, websites, or customer support portals. Unlike AI agents, most chatbots are reactive — they respond when prompted.
Types of Chatbots:
Use Cases of Chatbots:
Limitations:
Even AI-powered chatbots lack autonomous decision-making. They are effective for simple interactions but cannot manage complex or predictive workflows.
📊 Market Insight: The conversational AI market (chatbots + voice bots) is expected to grow from USD 10.7 billion in 2023 to USD 29.8 billion by 2028. This surge reflects how businesses are increasingly adopting chatbots to scale customer support and reduce costs.
Mini-Summary: Chatbots are best for simple, repetitive tasks like FAQs, lead generation, and 24/7 customer support.
Virtual assistants are digital tools like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant that help with daily tasks through text or voice commands.
Core Capabilities of Virtual Assistants:
Key Difference from AI Agents:
Example:
Mini-Summary: Virtual assistants handle daily productivity tasks, while AI agents handle data-driven automation and proactive problem-solving.
| Feature | AI Agents | Chatbots | Virtual Assistants |
| Core Function | Autonomous decision-making & problem-solving | Conversational support | Task execution & reminders |
| Proactivity | Proactive (acts without being asked) | Reactive (waits for user input) | Reactive (responds to commands) |
| Complexity | Handles multi-step workflows & predictions | Best for simple, repetitive tasks | Great for everyday personal productivity |
| Learning Ability | Learns & adapts continuously | Limited, unless AI-powered & retrained | Limited contextual learning |
| Best For | Business automation & predictive analytics | Customer queries, FAQs, lead generation | Personal task management & convenience |
| Examples | AI service agents, portfolio managers | E-commerce bots, customer support bots | Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant |
Your choice depends on goals, complexity, and customer expectations:
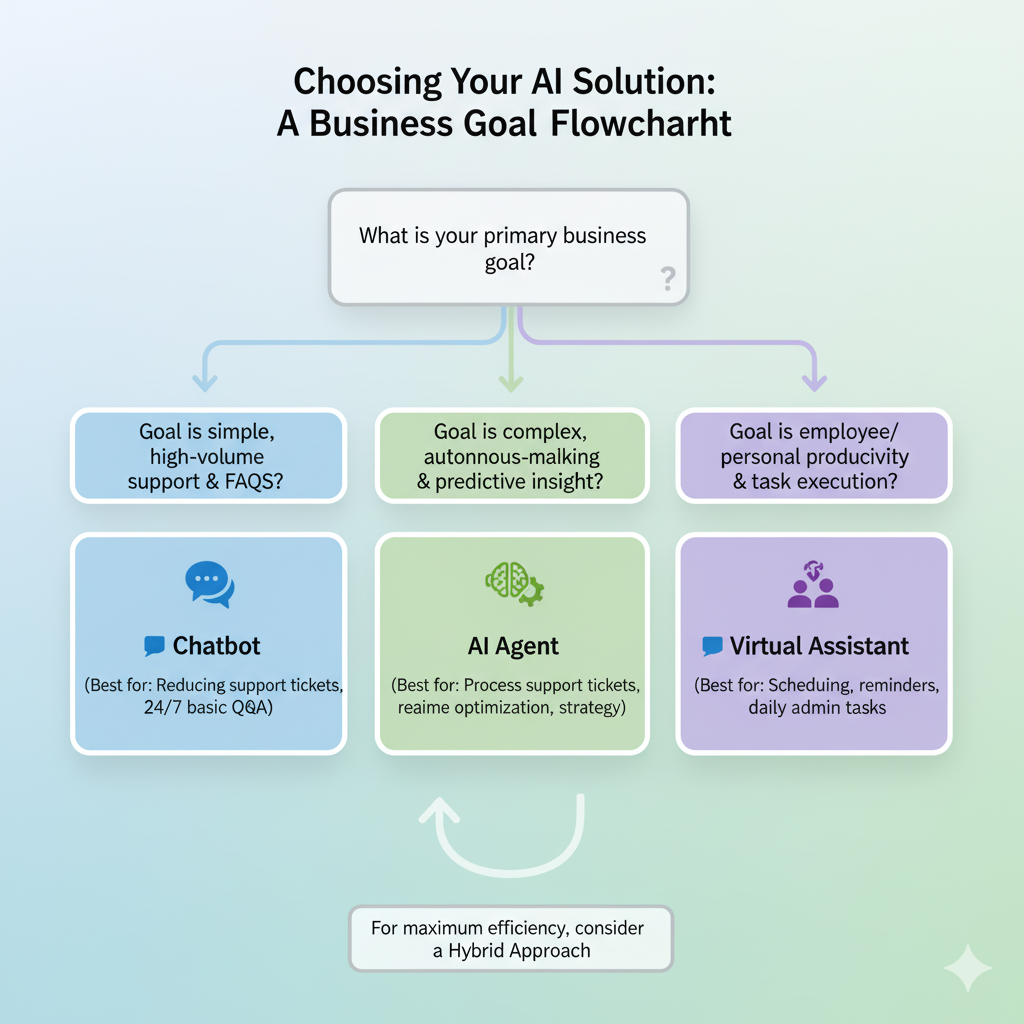
💡 Hybrid Approach: Many businesses combine them — chatbots handle customer FAQs, AI agents manage automation, and virtual assistants improve employee productivity.
The differences between AI agents vs chatbots vs virtual assistants can be summarized as:
Future Trend: With the conversational AI market projected to reach USD 29.8 billion by 2028 and the AI agents market expected to grow to USD 236.03 billion by 2034, businesses are rapidly shifting toward more autonomous and intelligent solutions. In fact, 92% of companies say they plan to increase AI budgets, showing that AI adoption is no longer optional — it’s essential for competitiveness. Ready to future-proof your business? At Gignaati, you can quickly and confidently hire AI agents to drive efficiency and innovation.
A chatbot is reactive, responding only when prompted. An AI agent is proactive, capable of learning from data, making decisions, and handling complex workflows.
Virtual assistants execute tasks like scheduling and reminders. AI agents analyze data, learn, and make proactive decisions, making them more strategic.
No. AI-powered chatbots use NLP for smarter responses, but they remain reactive. AI agents are fully autonomous and predictive.
Not entirely. Virtual assistants manage daily tasks, while AI agents handle complex, data-driven decision-making. Together, they complement each other.
AI agents use machine learning to improve continuously. Chatbots only learn if retrained, and rule-based bots don’t learn at all.
Consider task complexity and goals: choose chatbots for simple queries, AI agents for predictive automation, or a hybrid setup for maximum efficiency.
Explore Gignaati.com – where top AI innovators showcase verified AI agents for real-world solutions.
© 2025 Gignaati is a product of Smartians.ai. All rights reserved.