Have you ever wondered how Netflix recommends your favorite shows, or how Google Maps predicts traffic in real time? The magic behind these everyday conveniences is Machine Learning (ML). In today’s fast-paced digital world, Machine Learning isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a game-changer that powers everything from personalized marketing campaigns to advanced medical diagnostics. Let’s break it down in simple terms and explore what it means, the different types, popular tools, and why it’s shaping the future.
At its core, Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Unlike traditional software that follows rigid instructions, ML systems analyze data, identify patterns, and improve over time.
Think of it like teaching a child: instead of giving step-by-step rules, you show them examples until they figure it out on their own.
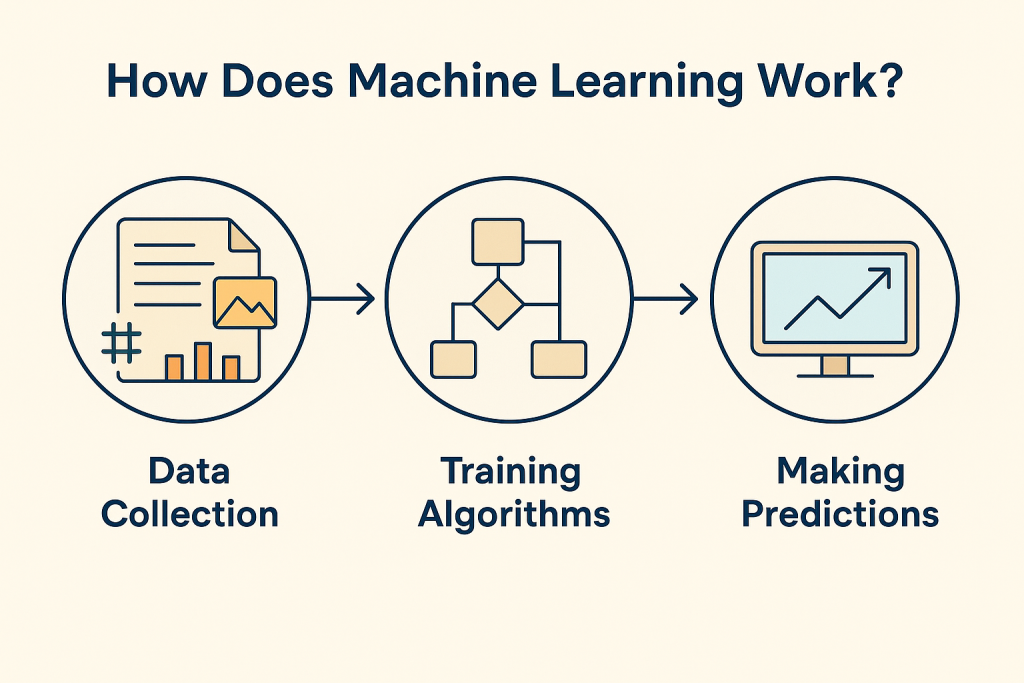
The process of ML can be simplified into three key steps:
Types of Machine Learning
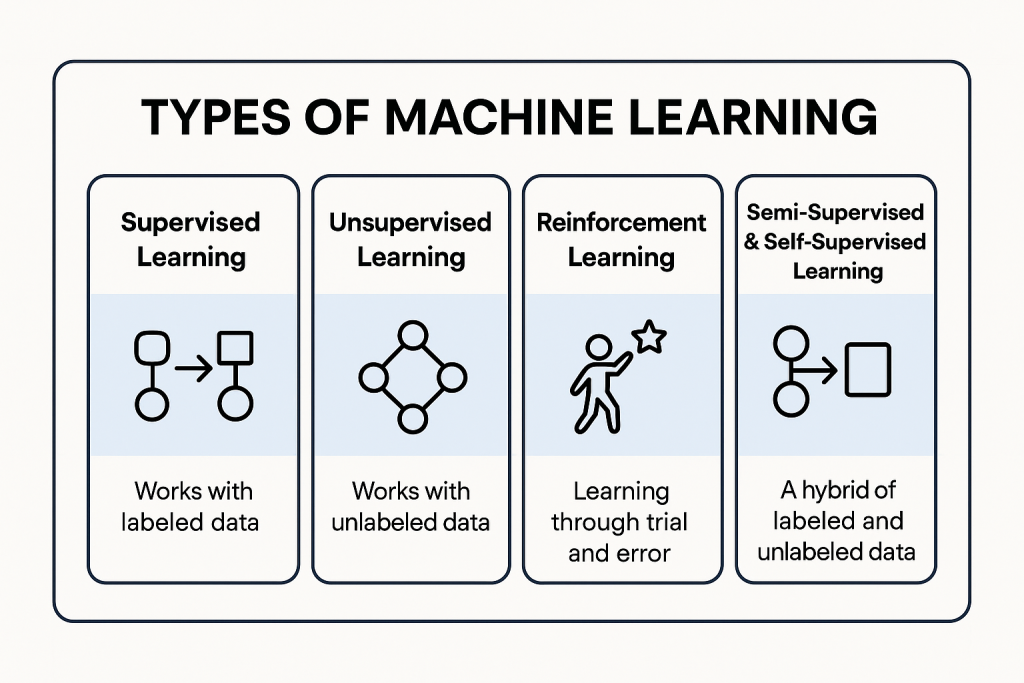
Machine Learning isn’t one-size-fits-all. There are several approaches, each suited for different problems:
If you’re exploring ML, these tools and frameworks are must-knows:
While these tools are powerful, mastering them requires structured learning and real-world practice. If you’re looking for guided, hands-on training, explore Gignaati AI Online Courses to build practical ML skills step by step.
Applications & Use Cases of Machine Learning
The impact of Machine Learning applications is everywhere:
As powerful as ML is, it isn’t perfect:
Businesses need to combine Machine Learning best practices with ethical AI principles to avoid pitfalls.
The future looks promising, with exciting trends on the horizon:
In the coming years, Machine Learning in business will be as fundamental as the internet is today.
Machine Learning is no longer confined to tech giants—it’s becoming an essential part of daily life and business strategy. Whether you’re in healthcare, retail, finance, or marketing, understanding Machine Learning can open new doors to growth and innovation.
If you want to dive deeper into how Machine Learning fits within the broader field of AI, check out our guide on the difference between AI and Machine Learning. It breaks down their relationship, unique roles, and why both are transforming the future of technology.
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that allows computers to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. Instead of following fixed instructions, ML algorithms recognize patterns, make predictions, and get smarter with more data. Common examples include spam filters, Netflix recommendations, and voice assistants.
The four main types of Machine Learning are:
Semi-Supervised / Self-Supervised Learning – combines labeled and unlabeled data.
Each type suits different problems, from predicting prices to customer segmentation.
Machine Learning works in three steps:
Prediction – the model uses learned patterns to make decisions.
For example, spam filters learn from thousands of emails to correctly classify future messages.
Some widely used Machine Learning tools and frameworks include TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-Learn, and Keras. These provide ready-to-use algorithms and deep learning capabilities. Cloud-based ML platforms such as Google Cloud AI, AWS Machine Learning, and Microsoft Azure ML also make it easier to scale projects for businesses and researchers.
Machine Learning is applied across industries:
Transportation: self-driving cars and traffic predictions
These applications show how ML enhances efficiency and personalization.
Machine Learning faces several challenges, including:
Scalability problems when handling big data
Businesses must pair ML innovation with ethical AI practices and strong infrastructure to overcome these challenges and ensure trustworthy outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broader field of creating machines that mimic human intelligence. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on learning from data. In short, AI is the overall concept, while ML is the method that powers many AI applications. For example, AI covers speech recognition, and ML provides the learning mechanism.
The future of Machine Learning includes trends like AutoML, which makes ML accessible for non-experts, Explainable AI for transparency, Edge ML running on devices like smartphones, and Generative AI for creating text, images, and music. As these evolve, ML will become as essential to businesses as the internet is today.
Explore Gignaati.com – where top AI innovators showcase verified AI agents for real-world solutions.
© 2025 Gignaati is a product of Smartians.ai. All rights reserved.